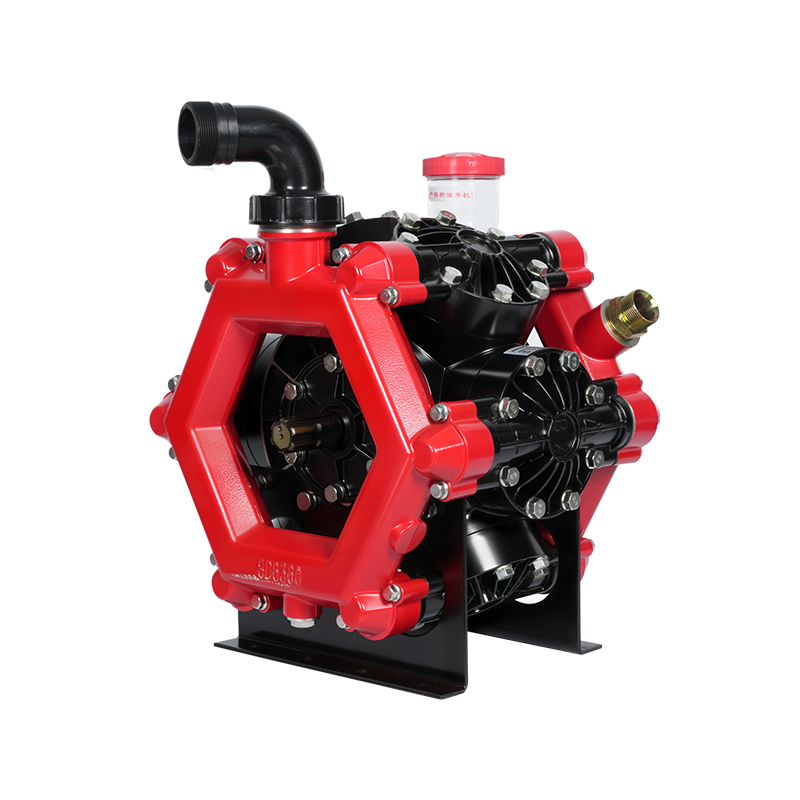
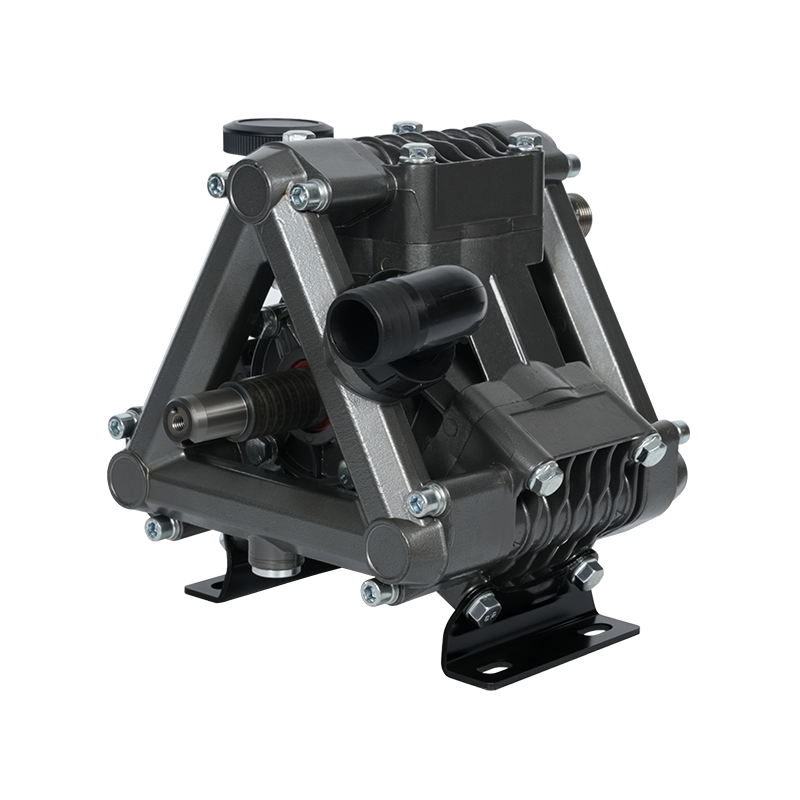
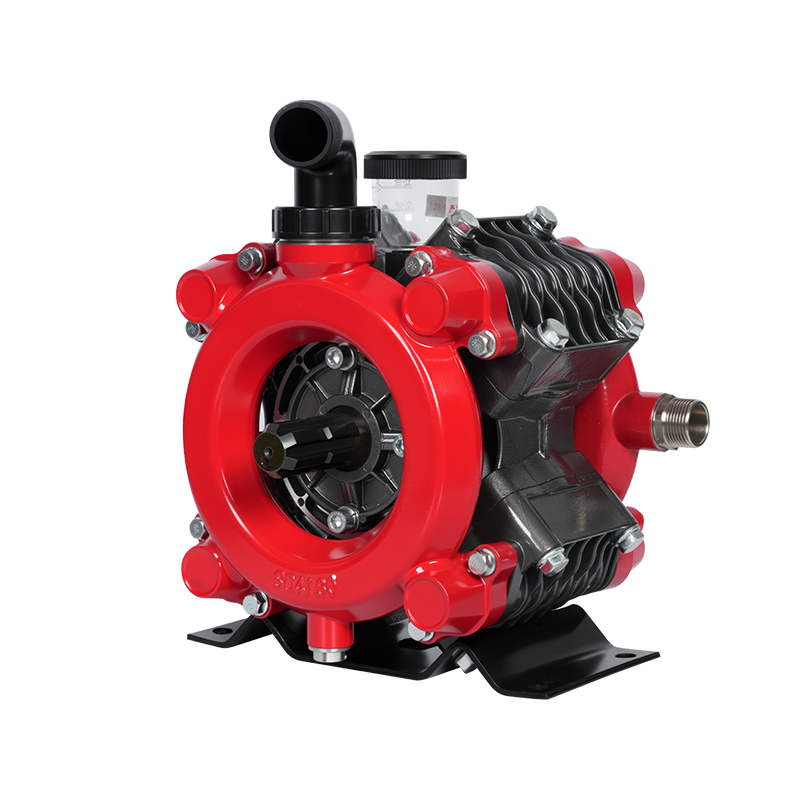
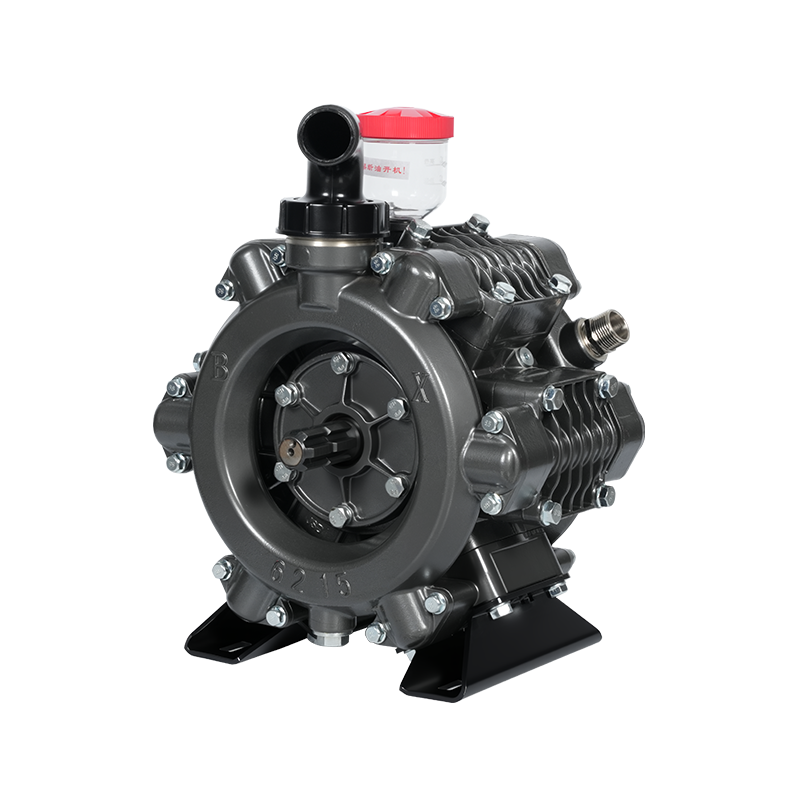
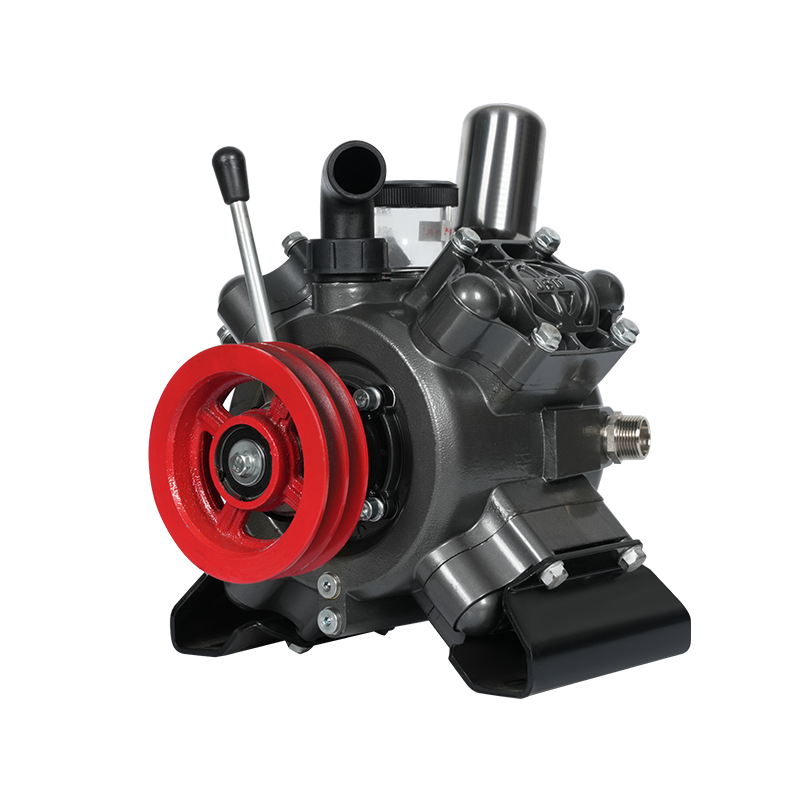
Developed based on advanced international technology, this new pump for plant protection machinery and disinfection features high operating pressure, stable discharge pressure, high flow rate, corrosion resistance, compact and rational structure, easy operation and maintenance, dehydration capability, and a wide range of applications. It can be combined with a variety of power equipment (such as electric motors, diesel engines, gasoline engines, tractors, and automobiles) to form various types of sprayers and misters. It is widely used for pest control in paddy and dry fields, orchards, forests, and urban gardens, as well as for spraying liquid chemical fertilizers and herbicides. In certain mountainous and hilly areas, it can also be used for small-scale farmland irrigation and drainage, high-altitude water diversion, and underground pipeline spraying. It can also be used in industrial fields such as vehicle cleaning, disinfection, chemical infusion, and environmental protection. It is currently an ideal new domestic industrial and agricultural pump.
-
 0m²
0m²Manufacturing Base
-
 0+
0+Patented Technologies


Jinhua Shuangding Machinery Co., Ltd. is a Diaphragm Pump For Pesticides Manufacturer and High Pressure Diaphragm Pump For Sprayers Company, specializing in the development Manufacture and sales of the brand "SHANG DING", "JIN SHUANG DING", "A-FARMERY" series of PTO diaphragm pumps, spray nozzles, spray pipes, control regulators that match different power equipment (such as electric motor, diesel engine, gasoline engine, tractor, and motor vehicle, etc) to form various models of sprayer.
Since our establishment, we have devoted ourselves to developing various PTO diaphragm pumps, spray nozzle sets, filters, and control regulators. Based on advanced technology and scientific management, a modern production line, complete test equipment, and a quality control system, our product quality improves.
-
Feb 24,2026
What Are Common Issues in a Diaphragm Pump For Pesticides System?
Modern agricultural spraying relies on stable pressure, predictable flow, and reliable chemical handling. A Diaphragm Pump For Pesticides fits these needs b...
-
Feb 20,2026
How Does a Crop Spraying Diaphragm Pump Perform Under Dry Running?
Crop protection spraying is not only about moving liquid from a tank to a nozzle. In real field work, operators deal with chemical corrosion, unstable press...
-
Feb 13,2026
How Does an Agricultural Sprayer Pump Handle Multiple Nozzles?
An Agricultural Sprayer Pump is not just a supporting component in spraying equipment. It directly influences application accuracy, spray stability, and che...
-
Feb 06,2026
How Does a Sprayer Diaphragm Pump Support Long Hose Spraying?
A Sprayer Diaphragm Pump is a core component in many power sprayers used for garden, agricultural, and landscape applications. Its role is not just to move ...
Why use a Diaphragm Pump for Pesticides?
Diaphragm pumps, specifically piston-diaphragm designs, have become a standard in modern agricultural spraying for a range of practical reasons. Their design and operational characteristics offer distinct benefits that align well with the demands of chemical application.
Chemical Compatibility: Constructed with materials like polypropylene, EPDM, and specialized seals, diaphragm pumps exhibit a high resistance to a broad spectrum of agricultural chemicals, including concentrated fertilizers, herbicides, and insecticides. This compatibility reduces wear and extends the pump's service life.
Ability to Run Dry: A significant operational advantage is their tolerance for running dry for limited periods. Unlike centrifugal pumps that can be damaged quickly without fluid, a diaphragm pump can survive brief dry runs, which can occur during tank refills or if a suction line becomes blocked, preventing immediate failure.
Self-Priming and High Pressure: These pumps are self-priming, meaning they can draw liquid into the pump from a tank located below the pump inlet. This simplifies setup and operation. Furthermore, they are capable of generating the high pressure required to operate multiple spray nozzles effectively, ensuring consistent spray patterns and droplet size across a wide boom.
Durability and Maintenance: The design isolates the hydraulic fluid from the chemical solution, protecting internal components from abrasion and corrosion. While diaphragms and valves are wear items that require periodic replacement, the process is generally straightforward, making field maintenance feasible and helping to control long-term operating costs.
What flow rate and pressure do I need?
The required flow rate is determined by your sprayer's boom width, travel speed, and application volume. Calculate the total nozzle output (in gallons per minute or liters per minute) needed to meet your agronomic goals. The pump must supply this flow while also maintaining the system pressure required for your nozzles to function correctly, typically between 40 and 150 PSI. Always select a pump with a flow and pressure rating that exceeds your calculated requirement to account for pump wear and ensure consistent performance.
How do I ensure chemical compatibility?
Chemical compatibility is critical for pump longevity. Examine the pump's construction materials, paying close attention to the diaphragm material (often EPDM or PTFE) and the housing and valve materials (such as polypropylene or stainless steel). Cross-reference these materials with the chemical resistance charts provided by the pump manufacturer against the specific pesticides and fertilizers you plan to use. Using an incompatible chemical can rapid deterioration of diaphragms and seals, causing premature failure.
What is the difference in diaphragm materials?
The diaphragm is a critical wear component. EPDM (Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer) is a common, cost-effective elastomer suitable for many herbicides and fertilizers. For more aggressive chemicals, including some solvents and strong acids, PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene or Teflon) diaphragms offer resistance but at a higher cost. The choice involves balancing the chemical resistance required for your specific application with the initial investment in the pump and its replacement parts.
How to troubleshoot a High-Temperature Diaphragm Pump?
A diaphragm pump that is operating at an excessively high temperature indicates an underlying issue that requires attention. Elevated temperatures can degrade hydraulic oil, damage diaphragms, and premature seal failure. The following steps can help diagnose and resolve the problem.
Inspect the Hydraulic Fluid and Valves
Check the oil level and condition: Low hydraulic oil is a primary cause of overheating, as it provides inadequate lubrication and cooling. Also, inspect the oil for contamination or a milky appearance, which suggests water ingress.
- Examine the oil relief valve: A malfunctioning or incorrectly set oil relief valve can cause oil to bypass internally, generating excessive heat through constant circulation under high pressure.
- Listen for chattering inlet or outlet valves: Worn or damaged valves can cause fluid to slip, forcing the pump to work harder to maintain pressure, which in turn generates additional heat.
Evaluate the Pump's Workload and Plumbing
- Assess the operating pressure: Continuously operating the pump at or near its rated pressure will naturally produce more heat. Verify that the system pressure is appropriate for the task.
- Check for flow restrictions: A clogged suction line, filter, or discharge line creates a significant pressure drop that the pump must overcome, increasing its workload and thermal output.
- Review plumbing design: Excessively long, narrow, or kinked hoses on either the suction or discharge side increase system resistance, contributing to the pump working under a higher load than necessary.
Examine Internal Wear Components
Inspect the diaphragms: Worn, torn, or hardened diaphragms reduce pumping efficiency. The pump motor must work harder to move the diaphragm, converting the extra effort into heat.
- Check the piston seal: On piston-diaphragm pumps, a worn piston seal can allow hydraulic fluid to leak past, reducing the effective stroke of the diaphragm and forcing the pump to cycle more frequently to achieve the same output.
- Look for internal friction: In cases, bearing wear or misalignment can create internal friction points. This direct mechanical resistance is a direct source of heat and often requires professional service or pump replacement.

 EN
EN  English
English 中文简体
中文简体 русский
русский





